 The most common reason of stenosis or occlusion of lower extremity is athersclerosis. Among the risk factors of atherosclerosis; smoking, high blood cholesterol level, cardio-vascular diseases in the family history, obesity, diabetes can be listed. Stenosis or occlusion of the leg arteries may not provide symptoms in early stages. The most common symptoms are cramp-style pains in the calves, thighs and the hip while walking, climbing stairs or running. This pain subsides in a period of resting. As the disease develops, distances of painfree walking are shortened and after a certain period, pain begin to continue while resting. In the next stage, non-healing wounds and gangrene will occur in toes. If this situation is not cured, it will end with the losing of the relevant foot or leg at different levels (amputation).
The most common reason of stenosis or occlusion of lower extremity is athersclerosis. Among the risk factors of atherosclerosis; smoking, high blood cholesterol level, cardio-vascular diseases in the family history, obesity, diabetes can be listed. Stenosis or occlusion of the leg arteries may not provide symptoms in early stages. The most common symptoms are cramp-style pains in the calves, thighs and the hip while walking, climbing stairs or running. This pain subsides in a period of resting. As the disease develops, distances of painfree walking are shortened and after a certain period, pain begin to continue while resting. In the next stage, non-healing wounds and gangrene will occur in toes. If this situation is not cured, it will end with the losing of the relevant foot or leg at different levels (amputation).
The patients coomplaints should be evaluted comprehensively . Then, pulses of the leg artery must be checked. Imaging methods are used in patients when necessary. Colored Doppler ultrasonography, MR or BT angiography or classical conventional angiography are most commonly used imaging techniques. Although angiography is still accepted as the first choice in vascular disease diagnosis, today's modern MR and CT devices can provide almost flawless results. In these methods, it is sufficient to have the patient enter the MR or CT device for a short period of 15-20 min. It is not necessary to puncture the groins as in the conventional angiography; contrast media is administered from the arm veins and spread to the whole body. The images of the desired zone, obtained in computer media, are then converted to angiography. Based on this imaging techniques, treatment method is decided. Medical treatment, endovascular method or open surgery are the treatmet options depending to the patient status.
Some of the patients can be monitored with certain intervals under medical treatment. In such patient groups, risk factors must be eliminated. Smoking must be quitted; if cholesterol values are high, those must be pulled back to normal levels through diets and medicines (statins). Overweight patients must lose weight and the blood sugar order of diabetic patients must be adjusted. Patients are directed to regular exercises under medicine treatment. Stenosis in leg arteries or short segment occlusions may be treated by endovascular methods (balloons or stents directed inside the blood vessel). In this method the artery is entered into, by a needle from the groin. It doesn't require general anesthesia, only local anesthesia is employed. Using angiography, the location and length of the stenosis or occclusion is determined. Then, in proper patients, the stenosis or occlusions are opened by special balloons or stents (metal pipettes placed in arteries). This method can be applied in the treatment of stenosis or occlusions of leg arteries, arm veins, internal organ arteriess ( kidneys and abdominal organs) and carotids arteries It is sufficient to have the patient rest at the hospital for one day. After being released, the patient can return to his/her work within 2-3 days.
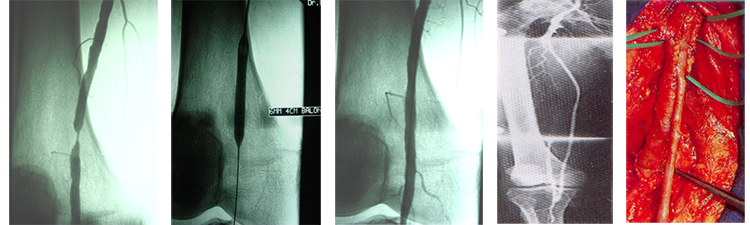
In occlusions effecting longer segments or which cannot be opened by endovascular methods, by-pass surgeries are necessary. These operations can be performed by spinal or epidural anesthesia ( below the waist). Therefore, patients with severe heart and lung problems easily have surgeries without the risk of general anesthesia. In these surgeries, an artificial vein suitable for the patient, or the patient's own vein is used for by-pass. The aim is to create a new blood flow tract and take enough blood flow to the tissues beyond the occlusion. After these kind of surgery the patient has to rest at the hospital for 3-5 days. After being released, the patient can return to his/her work within 10-15 days. All patients, who either had medical treatment, endovascular method or open surgeries must come back for control examinations at certain intervals.


 | +90 212 375 6565 / 6640
| +90 212 375 6565 / 6640